Before we install the Kubernetes components, we need to choose the runtime environment to handle the containers created by the Kubernetes objects(pod) and more specifically CRI( a plugin) OCI-compliant container runtime software that handles the communication between kubelet and runtime service. Once the container is created, individual containers can be created/stopped/started/removed independently. But if the containers are part of the Kubernetes controllers(replication controller, replicaset), then the desired state maintenance is part of the orchestration tool.
The most widely known container runtime is docker, however, this is not alone and we have other software available in the market CRI-O, CoreOS Rkt, etc and for more Comparison.
Here I have chosen, Docker as the container runtime interface for the k8s cluster.
I am going to follow the official docker documentation steps to install the docker on all the target machines. DockerOfficial
Three steps:
1. Remove old docker entries
2. Install docker
3. Start the Docker Service
Step1: Older versions of Docker were called docker or docker-engine, so let us uninstall all along with their dependencies.
Note: If this is a fresh installation and had no dependencies with existing processes then only attempt the remove old packages step. If anything required you can edit the list and run only that can be removed for this installation.
Login to Ansible-master machine and current working directory should be ~/k8s/playbooks, Check out previous lectures.
$ #Execute the below snippet and run the playbook.
cat <<EOF > docker-old-remove.yml
- name: create a Docker Runtime environment
hosts: all
become: yes
gather_facts: false
tasks:
- name: Remove if any existig old docker refernences
package:
name: "{{modules}}"
state: absent
vars:
modules:
- docker
- docker-client
- docker-client-latest
- docker-common
- docker-latest
- docker-latest-logrotate
- docker-logrotate
- docker-engine
- docker-selinux
- container-selinux
- docker-engine-selinux
register: dockerremove
- debug:
var: dockerremove.results
- local_action:
module: copy
content: "{{ dockerremove }}"
dest: ~/k8s/playbooks/{{inventory_hostname}}_docker_old_remove
EOF
$ ansible-playbook -i inventory docker-old-remove.yml --ask-become-pass
(you can make an inventory as default, check /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg)
Step2: Since we have removed old entries and now we can install a fresh copy of the docker on target machines.
$ # execute the snippet and apply the playbook as given below.
cat << EOF > docker-install.yaml
- name: setup the docker repository && yum-utils && install docker
hosts: master,worker
become: yes
gather_facts: no
tasks:
- name: install yum-utils
package:
name:
- yum-utils
state: present
tags: yumutils
- name: add the repository
shell: yum-config-manager \
--add-repo \
https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
args:
creates: /etc/yum.repos.d/docker-ce.repo
register: docker_repo_add
tags: dockerrepo
- local_action:
module: copy
content: "{{ docker_repo_add }}"
dest: /home/kubeadmin/k8s/playbooks/{{inventory_hostname}}_docker_repo_add
- name: install docker
package:
name:
- docker-ce
- docker-ce-cli
- containerd.io
state: present
update_cache: true
skip_broken: yes
register: dockerinstall
- debug:
var: dockerinstall.results
- local_action:
module: copy
content: "{{ dockerinstall }}"
dest: /home/kubeadmin/k8s/playbooks/{{inventory_hostname}}_docker_repo_add
EOF
$ ansible-playbook -i inventory docker-install.yaml --ask-become-pass
Step3: Now start the Docker service on all the target machines.
$ # execute the snippet and apply the playbook as given below.
cat <<EOF> docker-service.yml
- name: start the docker service
hosts: master,worker
gather_facts: no
become: yes
tasks:
- name: start docker service
service:
name: docker
state: started
enabled: yes
register: dockerstart
- local_action:
module: copy
content: "{{ dockerstart }}"
dest: /home/kubeadmin/k8s/playbooks/{{inventory_hostname}}_docker
$ ansible-playbook -i inventory docker-service.yml --ask-become-pass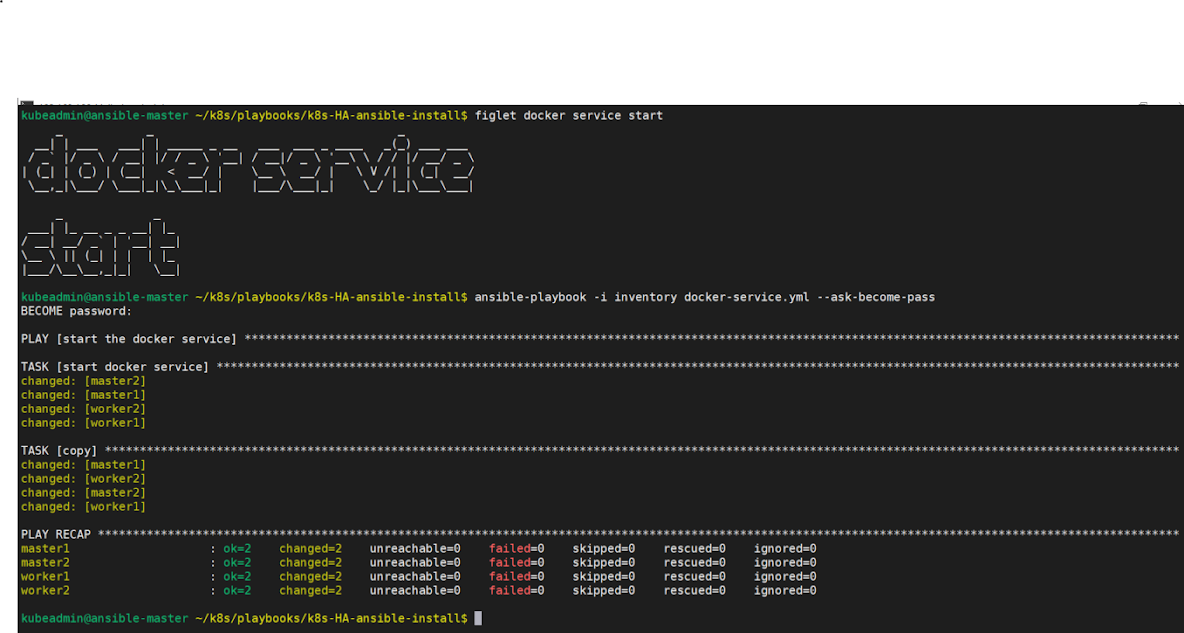
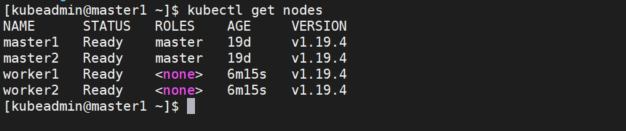
Successfully, we have installed the docker runtime and now it is time to set up the Kubernetes High available cluster with multi-master and Loadbalancer.



Comments
Post a Comment